Vietnamese fresh ginger: growing, care and harvesting techniques


Ginger is a herbaceous plant, 0.6-1m tall, dark green leaves 15-20cm long, about 2cm wide, smooth surface, slightly pale veins, leaves grow alternately, upright, with leaf sheaths, without stalk. Ginger is suitable for tropical climates, average annual temperature 21-27oC, annual rainfall 1,500-2,500mm. In particular, Ginger is suitable in places with altitudes below 1,500m above sea level.
In Vietnam, ginger is one of the crops that is easy to grow and brings high economic value. Ginger is used as a spice, essential oil and oleoresin, and is also used as an aromatic and flavor in the food and beverage industry and beverage.
Below are some steps in effective ginger growing techniques being applied by VIPSEN to achieve large and high-value ginger yields:
1. Planting land
Ginger plants need relatively good soil, thick, loose soil layer, few rocks, good water retention and drainage ability, ensuring adequate moisture during the plant’s growth. The best soil is loam, avoid sandy or clay soil. The most suitable PH level is 5.5-7.0.
Hilly, mountainous or upland land with high humus content is very suitable for growing ginger.
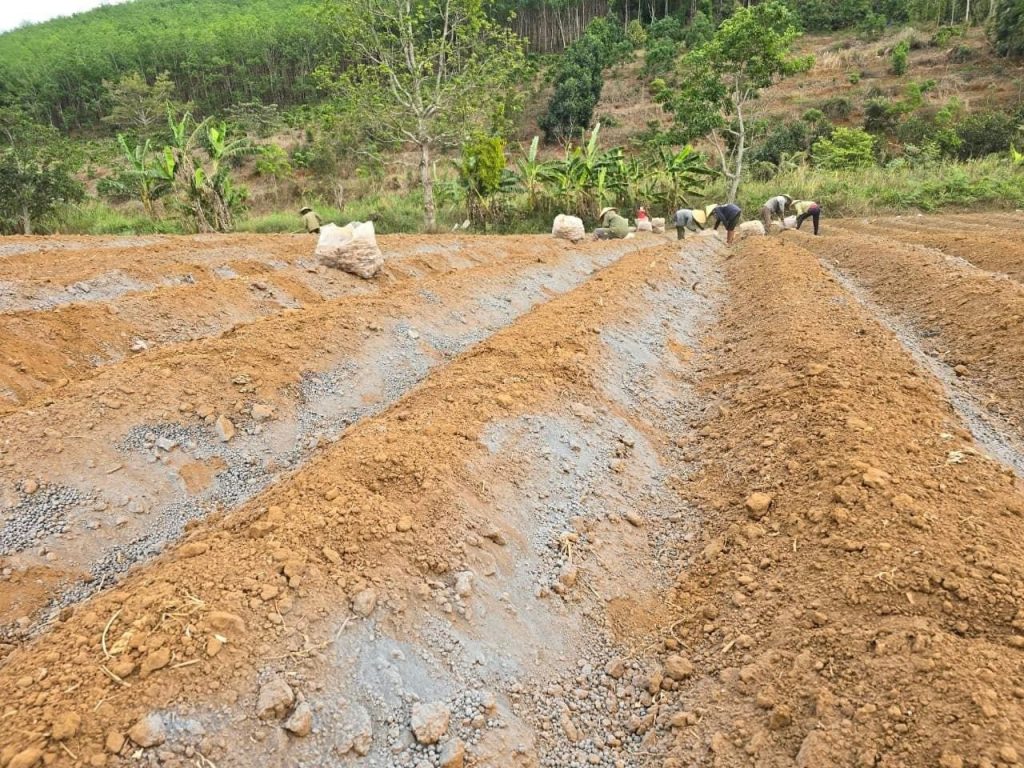

2. Land preparation
Thoroughly plough and hoe the land, make the beds along the parallel and the similar size lines, the length of the beds depends on the land, the width of the beds surface is from 70-80 cm, the height is 25cm.
3. Prepare ginger rhizome
In Vietnam, there are many varieties of ginger with good yield and quality, the most popular varieties are Buffalo ginger, Hybrid Peris ginger and Peris ginger. Depending on the conditions and goals of the producer, choose the appropriate ginger variety to grow. Good ginger root varieties need to meet a number of standards such as: The skin is old, shiny and fresh, plump, and has at least two sprout eyes.
4. Handling ginger rhizome before planting
Due to the large planting area, ginger rhizomes are nursed before planting. This helps the ginger seedlings to sprout evenly. After planting, ginger plants grow quickly and increase uniformity in ginger fields, making them easy to care for.
How to handle ginger rhizome: Choose old ginger roots (the main stem of a ginger branch or ginger root that is 9 months old or older), break or cut 3-4 cm long pieces of root (or branch), on each branch there must be at least 1 bud.
Handling ginger rhizome before planting: Moisturize, place ginger in layers, stack into piles, ensure drainage. Spray water on the ginger once every 2 days, cover the top with a layer of plastic wrap to maintain 80-90% humidity for the ginger.
Ginger root treatment is carried out 10-15 days before planting. When the ginger buds, it can be planted.

5. Planting season
Ginger plants grow best at temperatures above 20oC, high air humidity or drizzle. Therefore, the best ginger growing season for Northern provinces should be planted in the early spring, February to March every year.
6. Ginger growing techniques
Depending on the width of the bed surface, each bed is planted in 1 or 2 staggered rows. Hoe about 10 cm deep, with rows 40 – 50 cm apart and plants 30 – 40 cm apart (plant in bad soil thickly, plant in good soil sparsely).
Depending on soil quality, at the same time fertilize with composted manure and rice husk ash. Manure is composted for 1-2 months so as not to cause disease. Place the ginger rhizome (prepared in advance) 5 – 7 cm deep, with the sprout/bud eye facing up or horizontally, cover with fine soil and press firmly so that the soil has good contact with the root, then cover with fine soil to level the bed surface. .
After planting, cover the bed surface with a layer of straw to create porosity and retain moisture, preventing grass from growing.
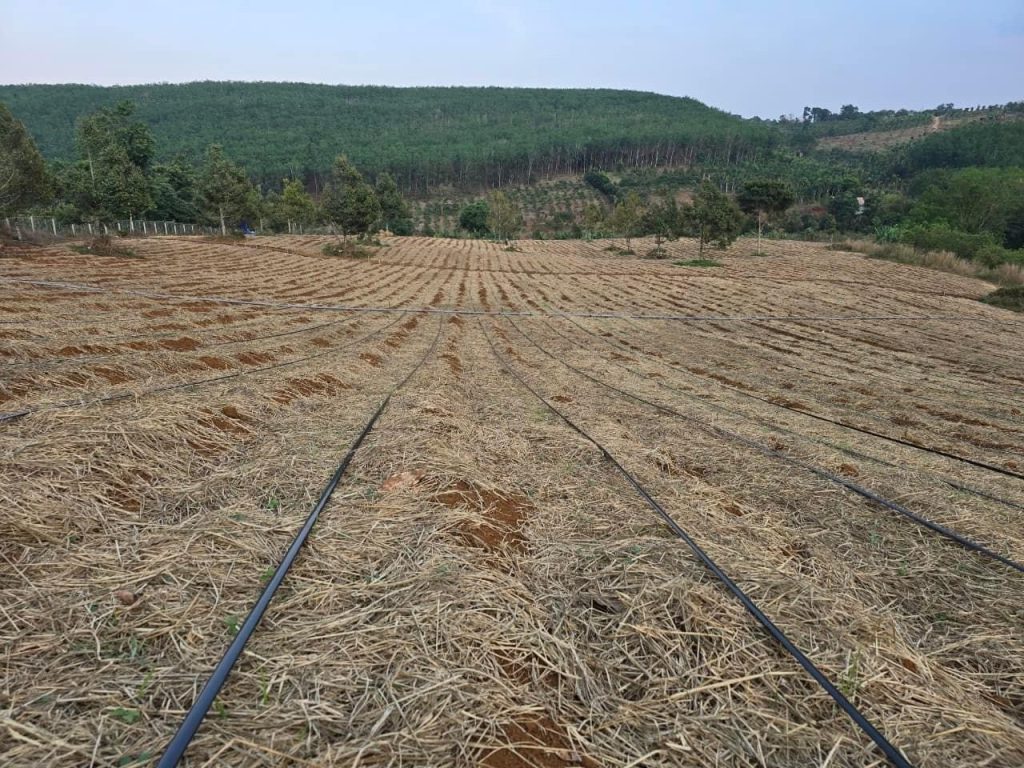

7. Ginger care techniques
After planting, if the weather is dry and cool, need to be watered to keep enough moisture regularly for the ginger to grow quickly, strongly, and fatly. It is necessary to add straw and rice husks to prevent grass from growing.
Depending on the level of intensive farming, soil nutrition and plant growth, fertilizer can be applied at the following levels:
– When the ginger grows 2 main leaves, soak phosphate fertilize with diluted manure to irrigate the ginger so it grows fat and branches well.
– Ginger begins to branch about 3-4 months after planting and the root form, then fertilize with decomposed manure and NPK..
Weeding combined with hilling to ginger root(in case the grass grows 4-5cm, it needs to be pulled up immediately).
How to fertilize: Stir the soil around, outside the root, spread fertilizer, cover with soil to the fertilizer and combine hilling with the root. Then water to help the plant absorb nutrients best.
8. Pest prevention
At the stage of new ginger buds, it needs to pay attention to snails biting the ginger plant tops. When detecting snails, catch them manually and do not use pesticides.
Ginger plants are susceptible to a number of diseases such as root rot, stem borers, leaf blight… Therefore, disease prevention and separation of diseased plants from the growing area need to be done immediately.
* Some measures to prevent and treat diseases for ginger plant:
– Plough and dry the soil before planting
– Choose the type of soil that drains easily
– Avoid planting during periods of heavy rain and wet soil, which increases the risk of plant infection.
– Use biological products to repel insects.
– Use beneficial microorganisms and antagonistic fungi to repel and cause disease in pests.
– Immediately after harvesting the previous crop or before start planting, it is necessary to clean the field and destroy excess stems (source of disease);
– Avoid leaving diseased plants near or throwing them into irrigation water sources to avoid spreading, arrange cultivation in a place that is not flooded.
– Apply organic fertilizer combined with biological product Trico (containing Trichoderma fungus)
– Apply lime to treat the soil and balance the pH (for acidic and alum soils)
– When seeing infected Ginger, it needs to localize and remove diseased plants, sprinkle lime on the diseased area to avoid spreading to a large area.
– When preparing soil for planting, only use tools and objects that do not carry pathogens or have been properly disinfected.
– The garden needs to have an isolation fence to prevent disease sources from entering and spreading.
– Limit vehicles, animals and visitors from entering the garden because the disease source can enter through infected soil that sticks to feet, animals, shoes, wheels, and care tools.
– Apply adequate fertilizer to improve plant health and resistance.
-…

9. Harvesting and preserving ginger
Harvest time: It is best to harvest Ginger after 9-10 months (after planting). The best time to harvest ginger root is December (should be harvested on a sunny day). During this period, ginger turns yellow and some leaves wither.
Prepare harvesting tools: Use hoes, baskets, and bags to harvest
Harvesting technique: When harvesting, pay attention to avoid scratching, breaking or crushing the roots. Hoe 20 – 25cm away from the root to keep the whole ginger clump, then gently pull out and shake off all the soil on the roots and put them in a new unused bag.
Preliminary processing, storage and transportation: Store ginger in a dry and cool place. When transporting, the vehicle must be cleaned, covered with a new tarpaulin sheet and carefully wrapped to ensure safe delivery to the place of consumption.
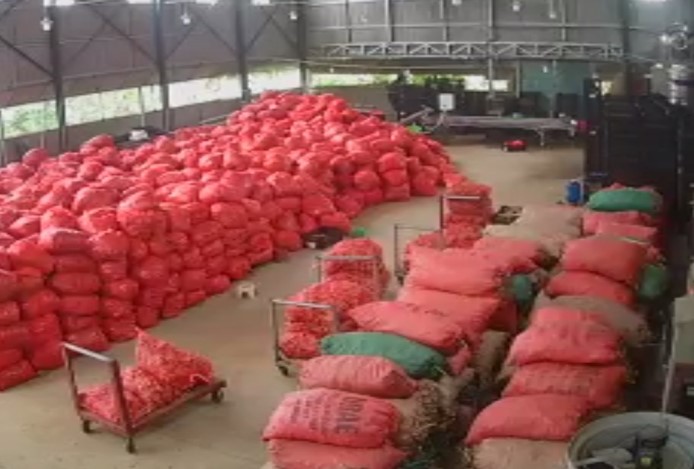

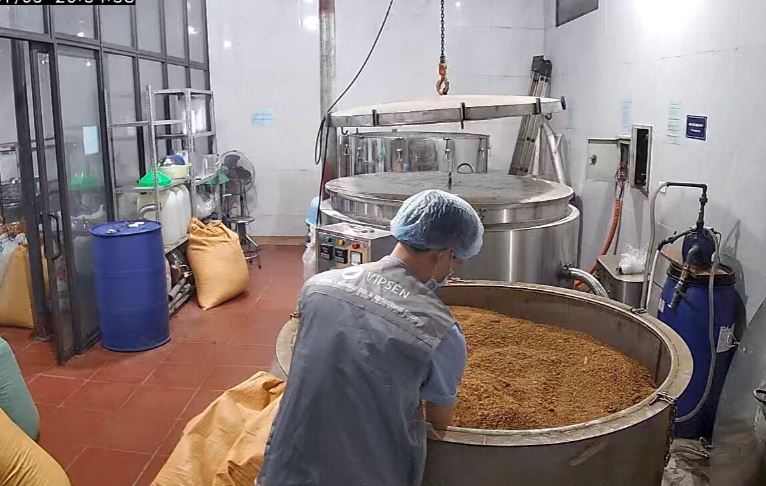
Packaged Ginger before loading up to container in VIPSEN ginger factory
10. VIPSEN’s ginger products
VIPSEN is one of the leading researchers, growers and producers agricultural spices in Vietnam. With a large growing area and teams of experienced agricultural experts, VIPSEN always guides and strictly controls the process from selecting plant varieties, planting, caring, harvesting and preserving. Spice agricultural products are processed and produced using advanced methods, applying science and technology to achieve high quality, large output and competitive price.
VIPSEN is producing and exporting ginger, cinnamon, and anise products, typical Vietnamese products. Regarding ginger, VIPSEN is bringing to domestic and foreign markets products such as: fresh ginger, dehydrated ginger slices, frozen peeled ginger, ginger powder, ginger essential oil and ginger oleoresin. Products are made from raw materials managed, harvested and selected by VIPSEN itself. With teams of experienced agricultural experts, VIPSEN is aiming to develop products that are certified by GlobalGAP and Organic (organic agriculture) to meet the increasing demands of the international market.
For further information, please contact:
Phone number/Whatsapp/Zalo/Wechat: +84 868 855 086
Email: Export@Vipsen.vn
Address: D7-TT9, Forosa street, Xuan Phuong new urban area, Xuan Phuong, Nam Tu Liem, Hanoi
Essential oil factory address: Bai Dai, Tien Xuan, Thach That, Hanoi, Vietnam
Address of ginger, cinnamon, and anise processing factory: Thu Do, An Tuong, Vinh Tuong, Vinh Phuc, Vietnam.