Vietnamese Organic Ginger: Techniques for growing and caring


1. Organic agriculture
1.1 What is organic agriculture?
Organic agriculture is a production system that aims to:
– Maintain the nutritional value of soil, water, ecosystems and protect human health.
– Protect the environment, absolutely do not use chemicals, pesticides, or chemical fertilizers
– Develop sustainable growing areas, bringing equal value to all participants.
– Provide high quality products, safe for human health.
1.2 General requirements
– The soil is not polluted due to the use of chemicals in previous years (chemical fertilizers, herbicides, pesticides…)
– For lands using chemicals for farming, a conversion period is required:
+/ For short-term crops, the conversion period from traditional farming land to organic farming land is 24 months
+/ For long-term crops, the conversion period is 36 months
– Cultivated land needs to be in a separate area, isolated from surrounding areas to avoid pollution. Other species can be planted to act as a buffer zone to prevent pollution from going downwind.
– Planting, care, and harvesting equipment must be new, clean, and unused
– Regularly record input materials and keep a farming diary
– Use Organic seeds and plant materials.
– Take measures to prevent the risk of surface erosion and saline soil.

2. Overview of Vietnamese ginger
2.1 Characteristics of Vietnamese ginger
Vietnamese ginger’s scientific name is Zingiber officinale, is a plant species of the Zingiberaceae family, widely used as a spice, or herbal medicine.
Vietnamese ginger is a small herbaceous plant that can reach a height of 0.6 – 1 m when growing. The rhizome swells, branches and grows horizontally. The leaves have long, no stem, pointed at the top and bottom, embracing each other to form a false stem. Leaves are 15 – 30cm long, about 2cm wide, smooth surface, white vein, fragrant.
The flowers of the ginger plant are often irregular. Ginger flowers grow in clusters, growing from rhizomes in October every year. The flower cluster’s stem can be 15 – 30cm long. The flowers are ovoid or cylindrical.
The whole plant, especially the rhizome, has a fragrant and hot taste.
In Vietnam, there are three main types of ginger commonly grown: Peris ginger, hybrid peris ginger and buffalo ginger. Among them, buffalo ginger has a fat body, few branches, and round branches that are easy to peel. This is the preferred ginger for the export market. Peris ginger, small root, many sharp branches, but more fragrant and spicy than other types of ginger.
2.2 Growing ginger
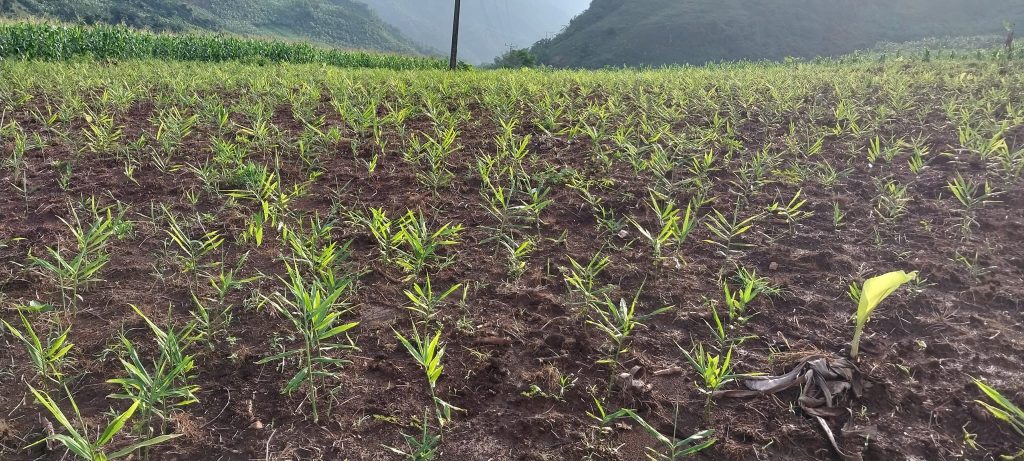
Ginger plants are grown with old roots, have sprouts and are harvested after about 10-11 months. The plant grows best in summer or fall when the climate is hot and humid. After a year of planting, if not harvested, the leaves tend to wither in winter and can regenerate from shoots emerging from the rhizome.
When harvested, the plant is pulled up and the root is cut, removing all sand and soil. Then ginger root is washed. People use it fresh or dry it.
2.3 Ginger growing areas in Vietnam
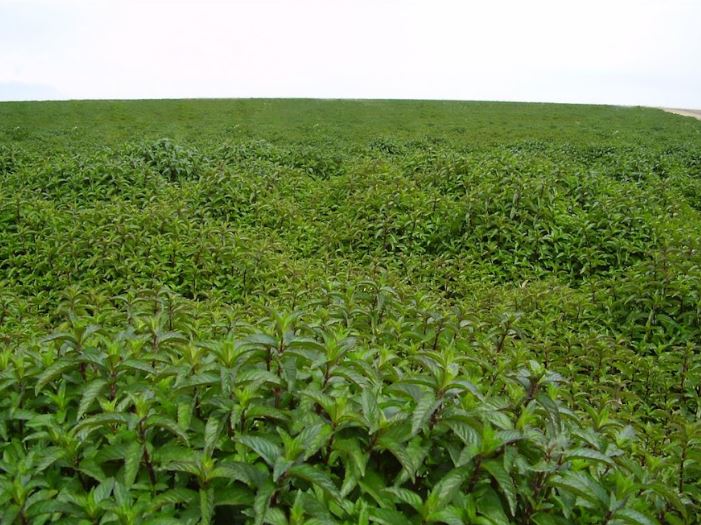
In Vietnam, ginger is grown in all provinces and cities across the country, from the mountains to the plains. However, ginger plants grow best in hills and mountains in places with loamy soil, good drainage and lots of light.
Ginger can be grown intercropped with other plants, but the efficiency is not high and requires a lot of fertilization to improve soil nutrition.

3. Techniques for growing and caring for Vietnamese Organic Ginger
3.1 Select planting area
– Choose soil with high humus content, loose, thick soil layer, few rocks, good water retention and drainage ability, and retains moisture throughout the growth period of the ginger plant. Prioritize choosing loose soil, soil mixed with sand, avoid planting on sandy or clay soil.
– The most suitable soil pH is 5.5-7, or can also choose soil with a lower pH of 4-5.5
– Ginger can also be intercropped under trees, with 20-30% coverage.
3.2 Planting season
– In the North, ginger is usually planted in the spring: around February-April every year. In the South, the best planting time is the beginning of the rainy season. It is about April- May every year.
– The growing time for exploitation is from 10-11 months
3.3 Prepare seeds
– Seedling ginger is old ginger over 10 months old, not infected with pests or diseases.
– Ginger seedlings need to be left in a cool place for about 1 week and then cut to the ginger cuttings by hand, not using a knife to avoid spreading pathogens.
– After 4-6 hours of breaking the cuttings, should arrange the parts evenly, with a bag underneath and a moist bag on top. After 2-3 days, cover with clean rotten straw, water and cover for about 1-2 weeks
– After 10-15 days, the ginger cuttings sprout and can be planted.
– Ginger varieties for planting need to be carefully selected: choose rhizomes with a diameter greater than 1.5 cm, free from rot, with 1-3 sprout eyes, and yellow inside the core.

3.4 Land preparation
– Ginger growing land needs to be weeded and cleaned.
– Plow and dry the soil to create porosity and kill pathogens in the soil
– Use lime powder to balance pH, disinfect and kill pathogens (50-60kg lime powder/1000m2) Sprinkle evenly on the bed surface 1 week before fertilizing
– Create a bed 120-150cm wide, about 35-40cm high. Sloping land should be arranged beds 40-50cm apart, holes 20-30cm apart. Apply fertilizer to the hole and cover with a thin layer of soil.
3.5 Planting techniques.
– Place the cuttings ginger in the holes, each hole has 1-2 cuttings, about 15-20cm from the bed surface and cover with a small, loose layer of soil until it is level with the bed surface, then press gently to make soil contact good with ginger cuttings.
– Ginger sprouts horizontally, so the root should be placed horizontally or along the planting row so that the buds can easily grow.
– After planting, cover the bed surface with leaves and straw to create soil moisture and add composted organic fertilizer.
3.6 Fertilizer
– Only use composted organic fertilizer. Absolutely do not use chemical fertilizers
– Amount of fertilizer: 3 tons of composted manure for 1000m2 of field
+/ Apply 2/3 of the above fertilizer before planting
+/ The remaining amount is top-dressing, combined with cleaning the grass and cultivating when the Ginger is 60-90 days old.
– Adding EM biological products (beneficial microorganisms) to promote the absorption of nutrients for Ginger and decompose insoluble substances in the soil, helping ginger grow healthily and prevent fungal diseases.
– Use manure and animal manure of natural origin, do not use manure from industrial livestock farms to avoid impurities remaining.

3.7 Care
– Two weeks after planting, ginger begins to grow buds and have young leaves. Proceed with weeding by hand and rooting when the ginger is 30-60 days old, 60-120 days old, 120-150 days old. Clean the grass and fill in soil around the ginger root.
– When weeding, avoid breaking ginger roots. Ginger with broken roots will have yellow leaves and gradually deteriorate.
– Ginger needs to be rooted and covered with straw to help retain soil moisture and reduce weed growth and increase the area for ginger branches to grow.
– Do not leave the ginger tubers exposed above the ground, as this will stop the ginger from growing and reduce the quality of the ginger after harvest.
4. Harvest ginger
4.1 Harvest time
– Harvest ginger after 9-10 months of age. When the leaves wither and turn yellow on about 2/3 of the area, that is a sign to proceed with harvesting.
4.2 Harvesting tools
Harvesting tools include: hoes, baskets, bags. All items must be new, separate and clean.
4.3 Harvesting techniques.
When harvesting, avoid scratching, breaking or crushing the tubers.
When digging, should keep the whole clump of tubers, hoe 20-25cm away from the root, then gently pull out and shake off all the soil on the tubers.
Healthy ginger, no worms, no spoilage. The ginger containers must be new, unused and fully stamped.

4.4 Transportation
Transport vehicles need to be cleaned and covered with new tarpaulins. Ginger needs to be carefully wrapped during transportation.
4.5 Preliminary processing and storage
Harvested ginger needs to be stored in a cool, dry place
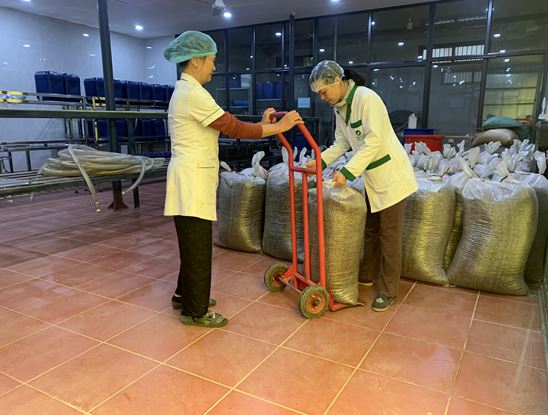
Separate storage for conventional ginger and organic ginger. There are signs to distinguish two different warehouses. If sharing a warehouse, there needs to be a partition and a distance between the conventional ginger area and the organic ginger area.
4.6 Packaging, labeling and storage
All bags, baskets, boxes, and trays containing organic ginger need to be stamped, labeled, and filled with complete information.
If cold storage is needed, the temperature and humidity need to be adjusted appropriately to avoid growing mold and bacteria.
Sample packing note is as follows:
Name of factory: …………………………………………………
Address:…………………………………………………………………
Phone:………………………………………………………………………
PACKING NOTE
Product’s name:
Science name:
Net weight………………….. Gross weight…………………………….
Batch code: ……………Manufacturing date……………. Expiry date…………….
Address of growing area: …………………………………………………………
Other parameters (Moisture content, classification, number of bags, storage requirements…) ………………………………………………………………..

5. VIPSEN ginger
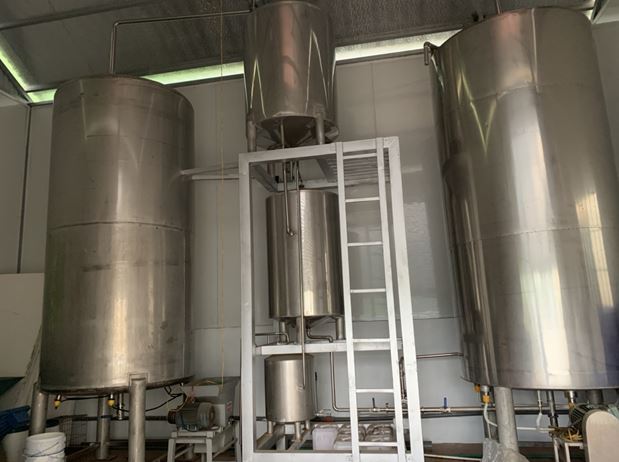
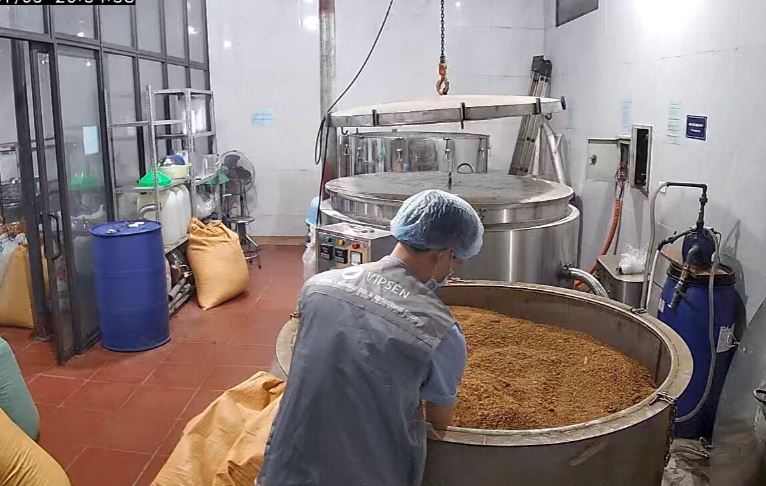
VIPSEN is one of the leading researchers, growers and processors of spice agricultural products in Vietnam. With a large growing area and a team of experienced agricultural experts, VIPSEN always guides and strictly controls the process from selecting varieties, planting, caring, harvesting and preserving. Spice agricultural products are processed and produced using advanced methods, applying science and technology to achieve high quality, large output at affordable prices.
VIPSEN is focusing on producing and exporting products of ginger, cinnamon, anise, essential oils and flavors extracted from typical Vietnamese plants. Regarding ginger, VIPSEN is bringing to domestic and foreign markets products such as: fresh ginger, dried ginger slices (dehydrated ginger slices), frozen peeled ginger, ginger powder, ginger essential oil and ginger oleoresin. Products produced from raw material areas are managed, harvested and selected by VIPSEN itself. With a team of experienced agricultural experts, VIPSEN is aiming to develop growing areas and produce products certified by GlobalGAP, Organic, JAS… to meet increasing demand of the international market.
For further information, please contact:
Phone number/Whatsapp/Zalo/Wechat: +84 868 855 086
Email: Export@Vipsen.vn
Address: D7-TT9, Forosa street, Xuan Phuong new urban area, Xuan Phuong, Nam Tu Liem, Hanoi, Vietnam.
Essential oil factory address: Bai Dai, Tien Xuan, Thach That, Hanoi, Vietnam
Address of ginger, cinnamon, and anise processing factory: Thu Do, An Tuong, Vinh Tuong, Vinh Phuc, Vietnam.